Identity and access management (IAM) is a crucial part of cybersecurity and risk management for any organization. It involves controlling and monitoring who has access to your business’s data, resources, and systems.
However, access management can also be complex and challenging, especially for large and growing enterprises with hundreds or thousands of collaborators, contractors, and other stakeholders. You must be able to quickly grant and revoke access to various applications and systems and track and audit access activity and compliance.
In this article, we’ll explain what access management is, why it’s crucial, and what some of the risks and challenges associated with it are.
We’ll also share a case study that illustrates the impact of poor access management in a real-world organization. Finally, we’ll introduce you to 1Password, a powerful and easy-to-use solution that can help you simplify and secure your access management process.
What is identity and access management?
Identity and access management is a security practice that focuses on controlling and monitoring access to an organization’s data, resources, and systems.
IAM helps you ensure that only the right person is authorized and has access to specific information. Or has the proper permission to perform certain tasks.
This process is more commonly known as the authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) premise in the cybersecurity industry.
Identity and access management typically involves three main components:
User authentication: This is the process of verifying a user’s identity when they’re trying to access a system or application. There are various authentication methods, such as passwords, biometrics, tokens, or certificates.
Role-based access control (RBAC) management: Managing RBAC means assigning roles and permissions to authorized users based on their job titles, functions, responsibilities, or the projects they’re involved in. RBAC helps you define what users can do and see within a system or application, such as read, write, edit, or delete data.
Access policy management and enforcement: This is the process of setting and applying rules and conditions that govern access to resources and systems. Access and password policies can include factors such as time, location, device, or network. Enforcement mechanisms can consist of logging, auditing, reporting, or alerting.
Why is access management important?
By implementing an effective IAM or identity and access management system, you can achieve benefits such as better security, operational efficiency, more effective collaboration, and regulatory compliance with industry standards.
Higher security
Access management helps you protect your business from unauthorized access, data breaches, and cyberattacks, which can be costly.
According to a report by IBM, each data breach cost companies an average of $4.45 million in 2023, almost $600,000 more than in 2020. It also took businesses an average of 277 days to identify and contain data breaches.
Moreover, 15% of the breaches were caused by stolen or compromised credentials. Thankfully, access management can help you reduce these risks and costs.
According to the same report, businesses that employ security automation throughout the organization, including identity and access management practices, see a reduction of 108 days in the data breach lifecycle.
They also see an average decrease in the cost per data breach of $1.76 million.
Operational efficiency and productivity
Access management helps improve your operational efficiency and productivity.
In many large organizations, employees are forced to manage many passwords to access different systems and accounts. The average person has to manage over 100 passwords. Entering so many passwords takes time, and updating or resetting them multiple times a year takes longer (anywhere from a few minutes to half an hour each). Consequently, the average employee spends 12.6 minutes per week entering or resetting passwords.
This adds up to 11 hours per year per employee of wasted time and frustration. For a large enterprise with 10,000 employees, this represents a loss of productivity of almost $3.3 million annually.
Access management can help you simplify and automate your password management process by providing your users with secure, convenient, and quick ways to authenticate and access their accounts via:
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA)
- Single sign-on (SSO)
- Passwordless login
Enhanced collaboration
Access management helps you enhance your collaboration and innovation across different workflows. Companies with a tight-knit collaboration culture are more likely to be high performing than those that don’t.
Access management can enable and support collaboration among your teams by providing them with easy and secure access to the tools and information they need to work together, such as cloud applications, shared documents, or project management software.
Regulatory compliance
Finally, identity and access management improves compliance with regulatory and industry obligations.
These obligations represent a challenge for organizations in all sectors. The top challenges include increasing volume, implementing regulatory changes, and balancing cost pressures.
According to the 2023 Cost of Compliance report by Thomson Reuters, almost three-quarters of financial firms expected an increase in the volume of regulatory information published by regulators and exchanges in 2023.
Access management can help you meet your compliance requirements and standards by providing the tools and capabilities to enforce and monitor your access policies, such as:
- Role-based access control
- Access logs
- Audit trails
- Reports
Access management risks
Despite the importance and benefits of access management, many organizations still face various risks and challenges when implementing and maintaining an effective IAM solution. Some of the common risks and challenges include:
Misconfiguration issues: Human error or the lack of implementation of best practices can lead to misconfigured systems, applications, or network devices. Improper settings or incorrect configurations may represent a security vulnerability, allowing attackers to gain unauthorized access and compromise sensitive data.
Excessive access privileges: Improper access management can lead to privilege creep, i.e., situations where users have more access than they need or should have, violating the Principle of Least Privilege (PoLP). These challenges frequently emerge during provisioning, de-provisioning, or granting access to third parties. They pose a significant problem for security and compliance because they can lead to data leakage, fraud, or abuse.
Insider threats: Insider threats are situations where users with legitimate access to an organization’s data or systems misuse or abuse their access for malicious or personal purposes. The lack of identity and access management at a granular level makes it challenging to detect and track the actions or threats of malicious insiders.
Social media data breach — An access management case study
To illustrate the importance and impact of access management, let’s look at a case study of an organization that suffered from poor access management practices and faced severe consequences.
Overview
In July 2020, one of the biggest digital platforms on the planet experienced a significant security breach that compromised 130 high-profile accounts. The attackers used these accounts to post fraudulent messages, asking followers to send Bitcoin to a specified address.
The cause: a weakness in identity access management
According to the company’s investigation, the breach was caused by a coordinated social engineering attack targeting some of its employees with access to internal tools and systems.
The first hacked account of an employee didn’t have access to all the internal systems the hackers needed.
However, it did have access to information about which systems the hackers needed to infiltrate and which employees had access to them, revealing a weakness in the company’s identity and access management.
Consequences of the data breach
The breach had significant consequences for the company involved, its users, and its stakeholders, such as:
- Legal and regulatory issues
- Reputation damage
- Financial losses
It opened the door for other security and operational challenges like having to temporarily lock down all verified accounts, suspend some of its features, and reset the passwords of the affected users.
The business also had to thoroughly investigate and review its security and access management practices and implement additional safeguards and controls to prevent future attacks.
Workforce access management for enterprise and business
As an enterprise or a business, you may have a large and diverse workforce that includes employees, contractors, partners, and customers.
You may also have a complex and dynamic tech stack that includes various applications, systems, and devices, both on-premises and in the cloud. You must be able to manage access to your workforce’s tech stack in a secure, efficient, and scalable way.
Here are some of the common challenges and pain points you may face regarding workforce access management.
Managing multiple user accounts and passwords
Your workforce may have to use various applications and systems, each with a different user account and password.
Managing multiple accounts can create a lot of hassle and frustration for your team.
Why? They have to remember and manage multiple passwords and deal with frequent password resets or lockouts. It can also create a lot of security risks, such as password reuse, sharing, or phishing.
Managing multiple access levels and permissions
Your team members all have different roles and responsibilities. Naturally, this will require different levels of access and permissions to various applications and systems.
This fact creates added complexity and confusion for your administrators, who must manually create, update, and delete user accounts and permissions and keep track of who has access to what.
It can also create security risks such as excessive access privileges, orphaned accounts, or unauthorized access.
Managing multiple authentication methods and factors
Your employees may have to use different authentication methods depending on the application, system, or device they are accessing.
For example, they may require passwords, biometrics, tokens, or certificates, creating inconsistency and inconvenience for your users. Why? They must switch between different authentication methods and carry or store multiple authentication factors.
To overcome these challenges and pain points, you need a workforce IAM system that can support the following features and capabilities:
Multi-factor authentication
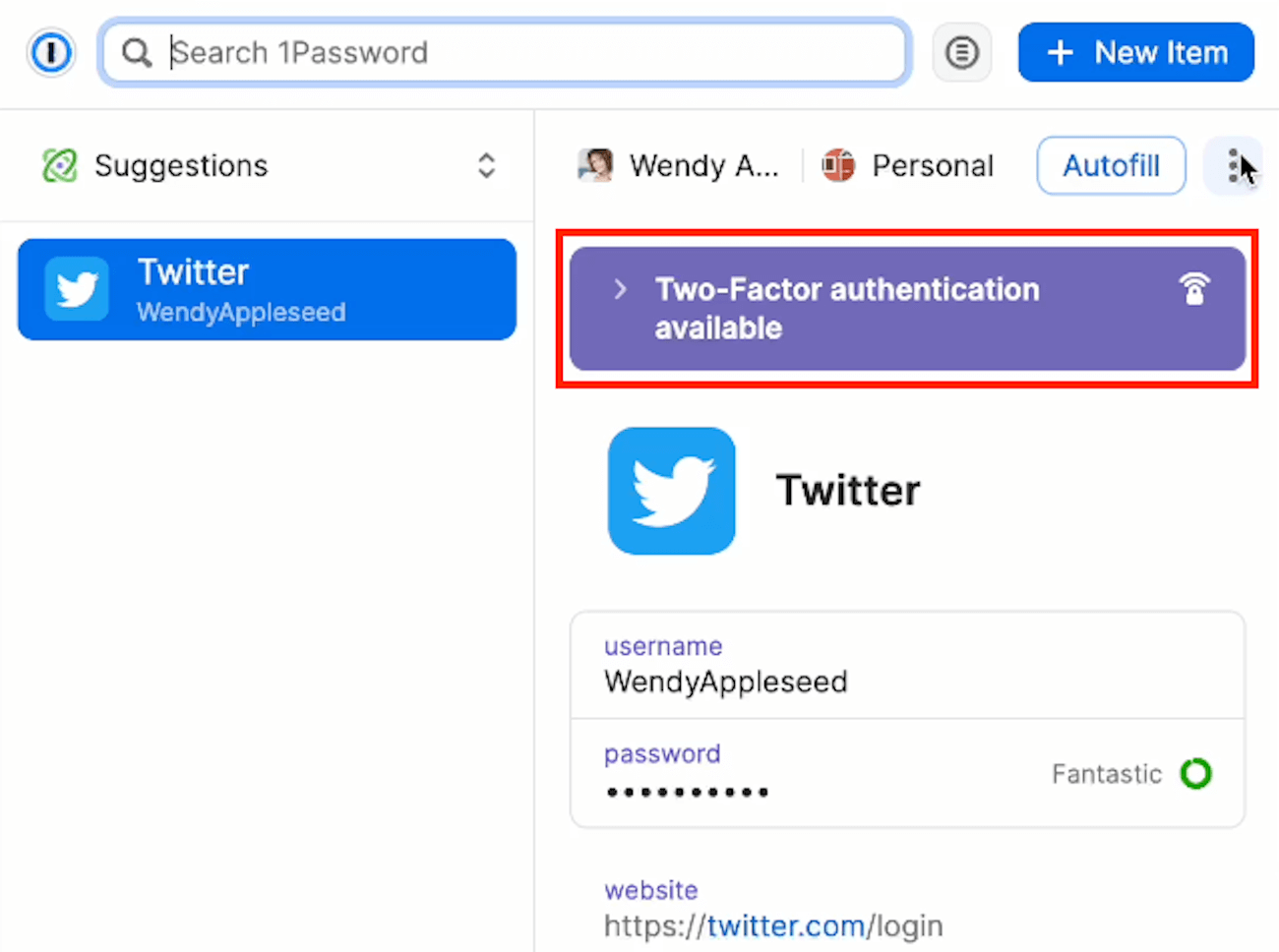
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is a security feature requiring users to provide more than one piece of evidence to verify their digital identity and access their accounts or systems.
The pieces of evidence can be anything from a password or a PIN to something the user has, such as a token, a smartphone, or a biometric factor.
Single sign-on
Single sign-on (SSO) allows users to access multiple applications and systems using one user account and password instead of many. You can implement SSO using various protocols and standards like SAML, OAuth, or OpenID Connect.
By providing access to multiple platforms using one set of credentials, SSO makes it easy for your team to manage multiple authentication methods and factors simultaneously.
SSO can also help you improve your operational efficiency and scalability by:
- Simplifying and automating your user account and password management process
- Reducing the workload and cost of your help desk
How to assess access management tools
When choosing an access management tool for your enterprise or business, you must consider several factors and criteria, such as:
Security: The tool should have a zero-trust architecture and provide you with robust and reliable security features and capabilities, such as MFA, SSO, and encryption. The tool should also comply with relevant security standards and regulations like ISO 27001, NIST, and GDPR.
Granular access and permissions: The ideal IAM tool will allow you to specify different access levels to various applications, platforms, or systems for each user. It should also track access and usage of the various stored credentials.
Usability: The tool should provide a smooth user experience, a user-friendly and intuitive interface, and functionality that’s easy to use and understand for your administrators and end users.
Scalability: Access management tools should also provide a flexible and adaptable solution that can scale up or down with your business needs and growth.
Integration: Finally, the tool should provide a seamless and comprehensive integration that can connect and work with your existing applications and systems, both on-premise and in the cloud.
1Password access management features
1Password is a password manager that offers more than just password storage and autofill. It also provides features and capabilities to simplify and secure your enterprise user management process while protecting user privacy.
Some of the 1Password access management features for businesses and enterprises include:
Autofill: 1Password will autofill almost any type of form item, including login credentials, answers to security questions, and MFA codes.
Two-factor authentication: You can configure 1Password to require your users to provide a second factor of authentication, such as a one-time password or a biometric, to access their accounts or systems.
Vault management: Manage and safeguard multiple accounts and passwords within an organization, ensuring enhanced security and streamlined access control.
Passkeys: This feature lets users access their accounts using special encryption keys stored in their devices, removing the need to create, memorize, or fill in passwords. With 1Password, your employees can store, sync, and share passkeys for a passwordless life while keeping your data safe.
Watchtower: The Watchtower feature serves as a security HQ. It monitors the websites you use and alerts end users and administrators if it detects that their passwords may have been compromised in a data breach. Watchtower also helps identify weak or reused passwords and alerts users to update accordingly.
Activity log: The activity log lets you view and export a detailed record of your users’ access activity and events, such as a login, logout, or password change.
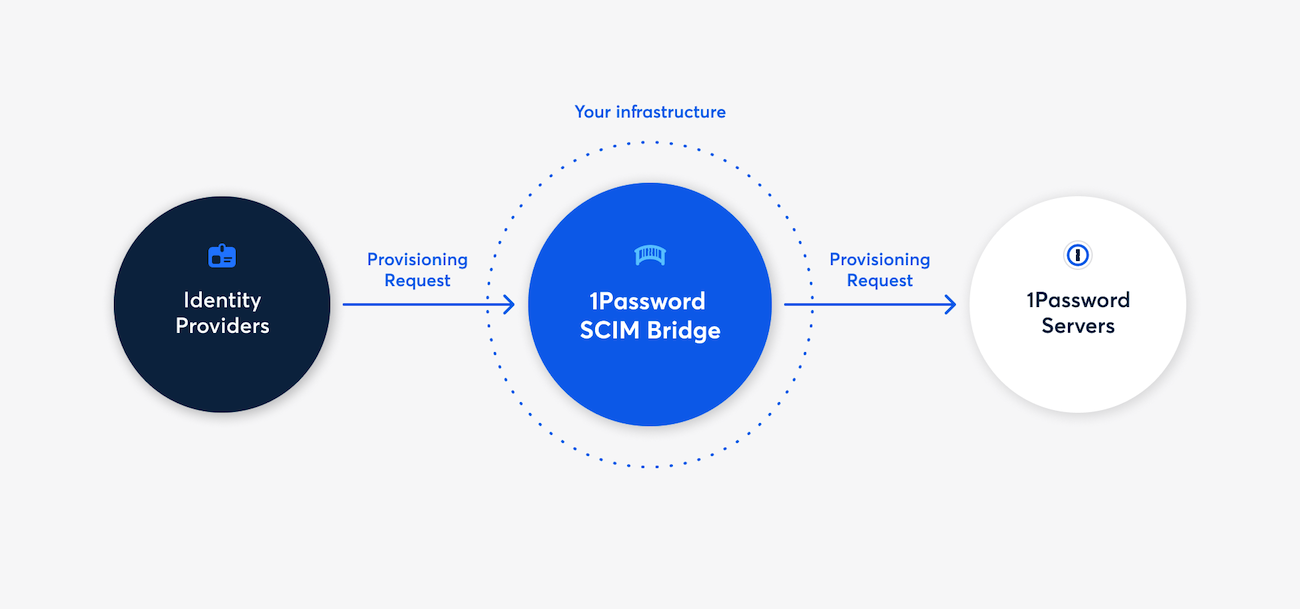
Automatic provisioning: You can connect 1Password to popular identity providers like Okta, Microsoft Entra ID, and Google Workspace through a 1Password SCIM bridge. Automated provisioning allows small businesses and large enterprises to automatically update access permissions to thousands of users with ease.
Secure your organization with 1Password
Over 100,000 businesses and large enterprises, including IBM, Slack, and Intercom, trust 1Password. It’s available both on-premise and in the cloud, and it supports various platforms and browsers, such as Windows, Mac, Linux, iOS, Android, Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge.
Ready to try 1Password for your business? Start your free 14-day trial today.
 by 1Password on
by 1Password on


Tweet about this post