This piece answers whether the built-in security of macOS is enough to forgo a third-party antivirus solution, and how admins can document that security for a SOC 2 audit.
Third-party malware detection and prevention (what we used to call antivirus) is not every Mac admin’s cup of tea. Some have bigger fish to fry (e.g., getting endpoint visibility); others are content with the built-in anti-malware capabilities of macOS and thus have no plans to deploy AV on its merits.
Unfortunately, SOC 2 and similar audits are forcing both types of Mac admins to purchase and deploy antivirus-like software earlier and earlier in their organization’s life cycle. When I ask IT admins who weren’t psyched about deploying AV why they did it anyway, their responses generally fall into two buckets:
They don’t believe macOS has sufficient anti-malware capabilities to pass a SOC2 audit.*
They cannot pass compliance audits like SOC 2 without enterprise reporting features around malware protection (which Apple doesn’t have for its AV features).
In this article, we’ll challenge both of these assumptions. Most importantly, I want to show that with open-source tools, you can pass a SOC 2 audit with the built-in anti-malware in macOS, while also being able to defend that position to senior leadership and auditors. To do that, I hope you’ll indulge me in shoving the third-party AV industry around a bit in the process.
*Compliance auditors get annoyed when you use binary terms like “pass” or “fail” to describe the outcome of an audit. Instead they use terms like “modified” or “qualified”. When I use the word “pass” in this article, I mean that you have obtained a SOC 2 report without negative qualifications.
Holistically, macOS' security is better than third-party AV
Ideally, before you face a SOC 2 audit, you truly believe you’ve made the best decisions possible when it comes to your Macs' security with the resources you have available. And as a security practitioner, I do actually believe that many organizations are better off relying on the built-in security capabilities of macOS without a third-party supplement. How can that be?
Well, for starters, the most basic and cursory research around third-party AV is a horror show of potential consequences that include: tanking an endpoint’s performance, regularly blocking legitimate software, indiscriminately selling users' data to undisclosed parties, and even the software itself becoming the source of major compromise.
Okay, but not every vendor is equally afflicted by these problems, so it’s not really fair to indict the entire third-party AV industry on a few anecdotes.
So now, let’s talk about what we mean by “better” security. Most AV security companies build their entire pitch based on a few measurements:
How fast can the AV detect novel/new threats?
How many real-time executions of bad things did the AV stop?
How many novel areas of visibility can it obtain?
Unfortunately, these measurements fail to consider the costs paid (usually by the end-user) for marginal improvements across these metrics.
But the end-user misery of third-party AV isn’t typically addressed until it becomes so egregious that it can be linked to a significant adverse financial event. To account for every form of misery that falls short of that bar, we need to adjust how we measure the AV’s actual performance.
Here is one way. Instead of just looking for the best antivirus performance at any cost, we need antivirus performance per unit of yuck, where “yuck” is defined as the qualitative degradation of the device’s user experience.
So who is better incentivized to give us maximum AV performance per yuck? In my view, it’s clearly OS vendors (like Apple), and here’s why:
OS vendors are financially impacted if users think their OS runs like junk.
OS vendors rely on a thriving third-party ecosystem of useful and fun software to drive the adoption of the OS itself. That means they must care deeply about how OS security impacts the viability of other software. Third-party AV does not have any incentive to care about the viability of other software until their customers notice (and then rectify it by just simply adding it to an allowlist).
OS vendors can use vertical integration to develop highly efficient security systems deep in the kernel of the OS itself, and rely on the existence of sophisticated security hardware like a TPM. Third-party vendors cannot safely hook in at this deep level , and they cannot successfully advocate for dedicated hardware within the device to make their technology better.
Given the above realities, it’s easy to see why Apple has upped macOS' built-in security capabilities considerably over the past few years.
XProtect
XProtect is macOS' built-in antivirus technology, which uses a standard industry format called YARA. Here’s an example of a YARA rule in the XProtect signature file:
rule EICAR
{
meta:
description = "OSX.eicar.com.i"
XProtect_rule = true
condition:
filesize <= 100000000 and hash.sha1(0, filesize) == "3395856ce81f2b7382dee72602f798b642f14140"
}
The above YARA rule looks for the existence of the famous ECIAR virus test file.
While this rule uses basic hash file matching (you can see more powerful examples in this repo from Scott Knight), YARA is a significant leg-up over traditional hash-only matching. Hash-only matching is very similar (if not identical) to how many classic AV vendors approach malware detection, but it fails as soon as the malware author changes a single byte of code.
The way YARA rules are put into practice is simple. Under the hood, it scans executables (when first launched or when they change) against a list of signatures. If a file matches any of the signatures, XProtect blocks its execution, generates logs, and finally alerts the user, advising them to put the offending executable to the Trash.
Another great benefit is that XProtect updates itself automatically, silently, and separately from manually installed security updates. When signatures are updated, XProtect will re-scan every subsequent app execution.
macOS' malware removal tool
Even if XProtect fails to stop malware from launching, you’re not doomed. macOS' Malware Removal Tool (MRT) remediates infections based on automated system data files and security updates from Apple, and continues to check for viruses and malware any time the user restarts or logs into the computer.
You may remember the MRT playing a significant role in the 2019 Zoom web server vulnerability. This is where Apple removed a vulnerable component of a third-party application using the MRT system.
Gatekeeper
Gatekeeper is an integral part of the entire anti-malware apparatus on macOS. It plays a critical role in checking executables' digital signatures to ensure they are coming from verified developers. This ensures that new executables that could be coming from unsafe sources (ex: apps from imposter websites) are handled to prevent them from harming the system until both the user and system can verify they are safe.
TCC permissions and System Integrity Protection
macOS 10.15 and above requires that all apps get users' permission before logging keystrokes or getting file, camera, or microphone access. Additionally, Apple stores macOS (Catalina and above) on a separate disk volume to separate essential system files from applications. As long as System Integrity Protection is enabled, these files cannot be modified by any processes.
Other macOS security features
In 2023, Apple began releasing Rapid Security Responses, a way of “applying security fixes to users more frequently by not requiring a full software update.” These updates typically happen in the background, but may occasionally require that users restart their computers.
Apple has also added a recording indicator to let users know if an app records their activities through the mic. Meanwhile, FileVault can encrypt data stored on a Mac.
Additionally, Safari uses anti-phishing technology to detect fraudulent websites and prevent plug-ins such as Silverlight, QuickTime, and Oracle Java from running if they aren’t updated to the latest version.
Perfect detection isn’t possible
When pitted against Apple’s comprehensive built-in security, AV vendors' common arguments come down to splitting hairs around detection efficacy.
The playbook generally involves the third-party AV vendor pointing to specific malware variants that their product can detect and that Apple failed to add to their signature lists promptly (or at all).
In my view, this is a foolish argument. It’s just as easy to find successful malware campaigns that no antivirus vendor could detect in a timely manner. Perfect detection/prevention is not possible, so we must consider the trust cost we wish to pay in terms of guaranteed performance degradation, false positives, and additional attack surface. If users are keeping a tight ship, applying updates, and not disabling Gatekeeper, there’s a very low chance that any other marginal improvements in protection will impact them.
Expanding upon the idea that prevention eventually fails, at some point, it makes sense to find a reasonable baseline for antivirus, and shift focus and resources into building a computer incident response plan. That means when (not if) a Mac does become compromised, the organization can better mitigate the potentially severe impacts of that compromise going unchecked.
The prevention game is one with serious diminishing returns per dollar spent. On the other hand, incident response is one of the best security investments you can make.
Compiling data to meet audit requirements
As we saw above, Apple does a reasonable job protecting Mac users from malware.
That’s great news! But there’s one problem.
You still need to collect data in order to compile reports for your compliance audit, and macOS doesn’t offer a way to achieve that level of fleet visibility.
That’s where osquery comes to the rescue.
You might have heard of using osquery to take device inventory, but did you know it’s also a handy tool for compiling data to meet SOC 2 reporting requirements?
How osquery supports SOC 2 compliance
Osquery is an open-source tool that allows users to query operating systems. For example, IT can use osquery to gain visibility into macOS, Windows, and Linux devices.
You can use osquery to check all the devices in your fleet. This allows you to ensure that they follow platform-specific rules based on your company’s data security policy and compliance standards (e.g., disk encryption, firewall status, OS updates, etc.)
Osquery can accumulate and log compliance data to support the SOC 2 reporting and the auditing process. You can see aggregated metrics or drill down to specifics using various filters to demonstrate that users' devices are compliant with SOC 2 requirements.
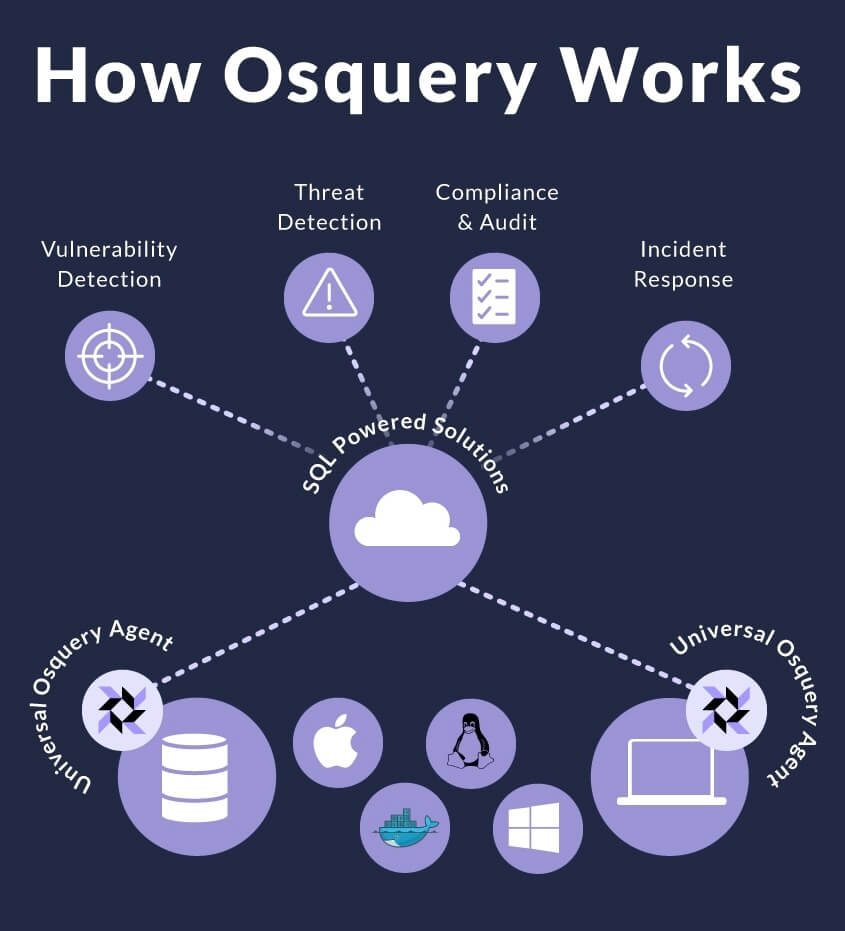
Many IT professionals favor osquery because it’s simple, reliable, and extensible. Since it works for all three major operating systems, you can collect data on every device in your fleet without using different tools.
How to use data collected by Osquery to support SOC 2
To pass your SOC 2 audit, you must create documentation to demonstrate that your systems and processes meet specific requirements.
For instance, to show that you have the appropriate defense against malware and viruses according to Common Criteria 6.8, you need a report describing your processes for file integrity monitoring (FIM) and endpoint security management.
Your documentation should demonstrate that:
You can track updates made to software and configuration files, and changes in endpoint protection statuses and events.
You have implemented controls to prevent, detect, and act upon unauthorized or malicious software introduced into your infrastructure.
Only authorized individuals can install applications and software on devices connected to your network.
You have processes to detect changes that could indicate the presence of unauthorized or malicious software.
There’s a management-defined change control process to monitor the implementation of software and applications.
Antivirus and anti-malware software is implemented and maintained to detect and remediate malware.
You follow procedures to scan information assets for malware and other unauthorized software.
Put osquery into action for SOC 2 compliance
macOS can satisfy the technical requirements for SOC 2 certification, without needing to use third-party antivirus. But it’s challenging for it to compile device data and report at scale. This is where osquery comes in: to provide fleet visibility, monitor activities, and compile the data you need to prove fleet compliance for SOC 2 audit and reporting.
To establish that the overall malware prevention apparatus of macOS is operational, XProtect (the primary component) requires that two things be present and functional for it to work correctly:
The first requirement is that Gatekeeper must be enabled for XProtect to run on recently downloaded executables (basically any file where the quarantine bit is set to “true”).
The second requirement is that System Integrity Protection (SIP) is enabled to ensure the anti-malware services and their definitions are not modified by a bad actor.
Below is a selection of simplified queries that 1Password® Extended Access Management’s osquery-based agent runs automatically to verify and document that XProtect’s requirements are met:
Osquery SQL: Is Gatekeeper enabled? What version is installed?
SELECT * FROM gatekeeper
+---------------------+----------------+---------+----------------+
| assessments_enabled | dev_id_enabled | version | opaque_version |
+---------------------+----------------+---------+----------------+
| 1 | 1 | 8.0 | 94 |
+---------------------+----------------+---------+----------------+
Osquery SQL: When was the last time XProtect signatures were updated?
SELECT date(mtime,'unixepoch') FROM file WHERE path='/Library/Apple/System/Library/CoreServices/XProtect.bundle/Contents/Resources/XProtect.plist';
+-------------------------+
| date(mtime,'unixepoch') |
+-------------------------+
| 2022-03-11 |
+-------------------------+
Osquery SQL: Has XProtect blocked the execution of known malware?
SELECT * FROM xprotect_reports;
+-----------------+-------------+------------+
| name | user_action | time |
+-----------------+-------------+------------+
| OSX.eicar.com.i | trash | 1650480090 |
+-----------------+-------------+------------+
Osquery SQL: Is MRT available? What version is installed?
WITH MRT_info AS (
SELECT * FROM plist WHERE path LIKE '/Library/Apple/System/Library/CoreServices/MRT.app/Contents/Info.plist'
)
SELECT
MAX(CASE WHEN path = '/Library/Apple/System/Library/CoreServices/MRT.app/Contents/Info.plist' THEN 'MRT.app' END) AS name,
MAX(CASE WHEN path = '/Library/Apple/System/Library/CoreServices/MRT.app/Contents/Info.plist' THEN '/Library/Apple/System/Library/CoreServices/MRT.app' END) AS path,
MAX(CASE WHEN key = 'CFBundleExecutable' THEN value END) AS bundle_executable,
MAX(CASE WHEN key = 'CFBundleIdentifier' THEN value END) AS bundle_identifier,
MAX(CASE WHEN key = 'CFBundleName' THEN value END) AS bundle_name,
MAX(CASE WHEN key = 'CFBundleShortVersionString' THEN value END) AS bundle_short_version,
MAX(CASE WHEN key = 'CFBundleVersion' THEN value END) AS bundle_version,
MAX(CASE WHEN key = 'CFBundlePackageType' THEN value END) AS bundle_package_type,
MAX(CASE WHEN key = 'LSEnvironment' THEN value END) AS environment,
MAX(CASE WHEN key = 'LSUIElement' THEN value END) AS element,
MAX(CASE WHEN key = 'DTCompiler' THEN value END) AS compiler,
MAX(CASE WHEN key = 'CFBundleDevelopmentRegion' THEN value END) AS development_region,
MAX(CASE WHEN key = 'CFBundleDisplayName' THEN value END) AS display_name,
MAX(CASE WHEN key = 'CFBundleGetInfoString' THEN value END) AS info_string,
MAX(CASE WHEN key = 'LSMinimumSystemVersion' THEN value END) AS minimum_system_version,
MAX(CASE WHEN key = 'LSApplicationCategoryType' THEN value END) AS category,
MAX(CASE WHEN key = 'NSAppleScriptEnabled' THEN value END) AS applescript_enabled,
MAX(CASE WHEN key = 'NSHumanReadableCopyright' THEN value END) AS copyright,
MAX(CASE WHEN key = '-- not_available' THEN value END) AS last_opened_time
FROM MRT_info GROUP BY path;
name = MRT.app
path = /Library/Apple/System/Library/CoreServices/MRT.app
bundle_executable = MRT
bundle_identifier = com.apple.MRT
bundle_name = MRT
bundle_short_version = 1.91
bundle_version = 1
bundle_package_type = APPL
environment =
element = 1
compiler = com.apple.compilers.llvm.clang.1_0
development_region = en
display_name =
info_string =
minimum_system_version = 10.10
category =
applescript_enabled =
copyright = Copyright © 2020 Apple, Inc. All rights reserved.
last_opened_time =
Osquery SQL: Is System Integrity Protection (SIP) turned on?
SELECT * FROM sip_config;
+----------------------------+---------+---------------+
| config_flag | enabled | enabled_nvram |
+----------------------------+---------+---------------+
| sip | 1 | 1 |
| allow_apple_internal | 0 | 0 |
| allow_device_configuration | 0 | 0 |
| allow_kernel_debugger | 0 | 0 |
| allow_task_for_pid | 0 | 0 |
| allow_unrestricted_dtrace | 0 | 0 |
| allow_unrestricted_fs | 0 | 0 |
| allow_unrestricted_nvram | 0 | 0 |
| allow_untrusted_kexts | 0 | 0 |
+----------------------------+---------+---------------+
As you can see above, osquery can help collect important details about the state of macOS' built-in malware and virus protection. The question now becomes: how do you best aggregate that data for auditors?
Osquery out of the box emits logs that can be aggregated by third-party SIEMs and log aggregation tools. Using their native reporting functions, you can build a dashboard that will get you through your audit and give you incredible visibility.
If you don’t want to build all this yourself, 1Password Extended Access Management can get you up and running fast. Our Device Trust solution automatically gives you native osquery installers for Macs, Windows, and Linux devices. Once the device trust agent runs, it will automatically collect all the pertinent info, aggregate it, and visualize it.
Within minutes, IT admins can look at a dashboard reporting on the XProtect configurations of every macOS device in their fleet. From there, they have the necessary assurance and reporting to prove compliance to their SOC auditors.
Another question vanilla osquery doesn’t have any answer for is remediation. For example, if you find that Gatekeeper or SIP is disabled, how do you fix them? One approach is to use an MDM to force something like Gatekeeper to be enabled. Unfortunately, other settings like SIP cannot be managed by these types of policies.
Again, 1Password Extended Access Management can run checks against your Macs to verify that these services are enabled. If they aren’t, users are blocked from accessing company resources until they’ve fixed the issue.
We achieve this through end-user remediation, instructing users on how to re-enable those features (while explaining why it’s important to keep them that way). For instance, remember those Rapid Security Responses from earlier? In the cases where they require updating your computer, 1Password Extended Access Management’s agent can see which users haven’t updated, and then instruct them on how to do so. From there, users have a deadline on when they need to install the update, or else they’ll be locked out of company systems. And unlike MDM, you can apply this approach to device trust to unmanaged, BYOd-devices.
End-user remediation is a part of our Honest Security philosophy. We believe that teaching end-users how to keep their devices secure nets better and more complete security than any AV scan ever could on its own.
To see how 1Password Extended Access Management can secure your fleet and achieve 100% compliance, reach out for a demo.
 by Jason Meller on
by Jason Meller on